Screens are everywhere. Phones, laptops, televisions, tablets, and even car dashboards. We look at them for hours every day. Yet most people do not fully understand what “display resolution” means when buying a new device. Labels like 720p, 1080p, 4K, and 8K appear on product boxes, but the numbers alone do not tell the full story.
Display resolution is only one part of image clarity. Screen size, viewing distance, and pixel density matter just as much. A 4K resolution on a small phone may look almost identical to a 1440p screen at normal viewing distance. Meanwhile, a large television benefits greatly from moving from 1080p to 4K.
This guide explains display resolution in plain language. No marketing terms. No unnecessary technical jargon. You will learn what each resolution standard means, how many pixels it contains, and where each one makes practical sense. By the end, you will be able to choose a screen based on real understanding rather than just bigger numbers.
If you want to instantly check your current screen’s resolution, you can use the Screen Resolution Checker.
Also Read: WhatisMyScreenResolution Blog
Core Concept Explanation

Display resolution describes how many pixels a screen can show. It is written as width × height. For example, 1920 × 1080 means the screen displays 1,920 pixels horizontally and 1,080 vertically. Multiply them, and you get the total number of pixels forming the image.
More pixels allow finer detail. But higher resolution also requires more processing power and more data for video playback. This is where practical judgment matters.
Resolution alone does not guarantee a better experience. A small screen with extremely high resolution can waste processing power without visible improvement. A large screen with low resolution will look soft and pixelated.
In simple terms:
Resolution should match the job the screen is doing.
What Is Screen Resolution?
Screen resolution refers to the number of individual pixels displayed on a screen. Each pixel is a tiny point of color. When combined, they form text, images, and video.
Higher resolution means
Lower resolution means
Another important factor is pixel density (PPI – pixels per inch). A small high-resolution screen may look sharper than a large low-resolution screen even if both share the same resolution.
If you want to calculate pixel density for any screen size, use our PPI Calculator.
Common Display Resolutions
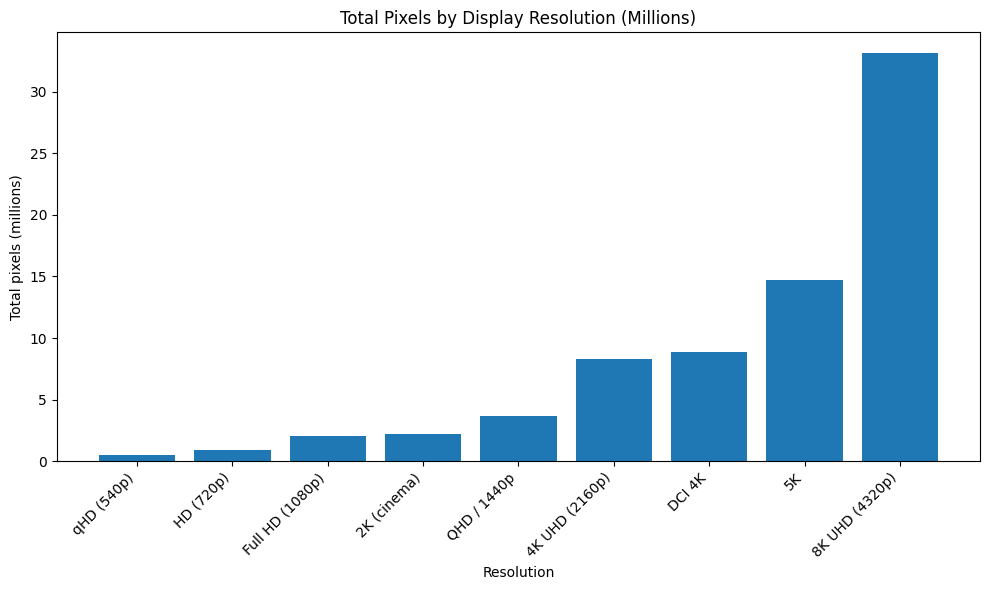
The landscape of display resolutions has evolved dramatically. The following table provides a clear overview of the most common standards you’ll encounter today.
|
Resolution Name |
Standard Abbreviation |
Dimensions (Width × Height) |
Total Pixels |
Typical Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Quarter High Definition |
qHD / 540p |
960 × 540 |
5,18,400 |
16:09 |
|
High Definition |
HD / 720p |
1280 × 720 |
9,21,600 |
16:09 |
|
Full High Definition |
Full HD / FHD / 1080p |
1920 × 1080 |
20,73,600 |
16:09 |
|
2K |
2K / DCI 2K |
2048 × 1080 |
22,11,840 |
≈19:10 |
|
Quad High Definition |
QHD / WQHD / 1440p |
2560 × 1440 |
36,86,400 |
16:09 |
|
4K Ultra High Definition |
4K UHD / 2160p |
3840 × 2160 |
82,94,400 |
16:09 |
|
Cinema 4K |
DCI 4K |
4096 × 2160 |
88,47,360 |
≈19:10 |
|
5K |
5K |
5120 × 2880 |
1,47,45,600 |
16:09 |
|
8K Ultra High Definition |
8K UHD / 4320p |
7680 × 4320 |
3,31,77,600 |
16:09 |
Display Resolution Explained
qHD (540p – 960 × 540)
qHD stands for quarter HD. It appears on entry-level smartphones and small devices. It consumes less battery and bandwidth but offers basic clarity suitable for everyday use.
HD (720p – 1280 × 720)
720p was the first widely adopted high-definition standard. It remains common in budget TVs, older laptops, and low-bandwidth streaming. It provides acceptable clarity on smaller screens.
Full HD (1080p – 1920 × 1080)
1080p, also called Full HD, is still the most common resolution worldwide. It balances sharpness, performance, and content availability. Most laptops, monitors, and TVs use this standard.
2K (2048 × 1080)
In cinema production, 2K refers to 2048 × 1080 pixels. In consumer marketing, the term is sometimes used incorrectly for 1440p screens. Always check pixel dimensions to avoid confusion.
1440p (QHD / WQHD – 2560 × 1440)
1440p offers noticeably sharper text and images than 1080p. It is popular in gaming monitors and premium smartphones. It provides more workspace without the heavy hardware demands of 4K.
4K UHD (2160p – 3840 × 2160)
4K UHD contains four times as many pixels as 1080p. It is now the standard for modern televisions and professional video work. Streaming services and game consoles widely support 4K content.
5K (5120 × 2880)
5K displays are mainly used in high-end monitors and creative workstations. They allow editing 4K content at native resolution while keeping workspace for tools and timelines.
8K UHD (7680 × 4320)
8K is the highest consumer display resolution currently available. It delivers extreme detail on very large screens. Native 8K content is still limited, but upscaling is improving.
Common Use Cases by Resolution
Choosing the right resolution depends heavily on your primary activities. The following table matches resolutions with their ideal applications to guide your decision.
| Primary Use Case | Recommended Resolution(s) | Key Reason |
| Competitive Esports Gaming | Full HD (1080p) | Maximizes frame rates and responsiveness on high-refresh-rate monitors. |
| General Office & Web Use | Full HD (1080p) or QHD (1440p) | Provides clear text and ample space for windows at a reasonable cost. |
| High-Fidelity/Immersion Gaming | QHD (1440p) or 4K UHD | Excellent detail and visual effects; 1440p offers a great performance/quality balance. |
| Streaming Movies & TV Shows | 4K UHD | Matches the highest resolution offered by major streaming platforms (Netflix, Disney+). |
| Professional Content Creation | 4K UHD, 5K, or 8K UHD | Necessary for editing 4K/8K video, high-res photography, and detailed graphic design. |
| Console Gaming (PS5 / Xbox Series X) | 4K UHD | Leverages the full output capability of modern consoles on compatible TVs/monitors. |
| Smartphone Media Viewing | QHD+ (1440p variants) or FHD+ | High pixel density (PPI) ensures razor-sharp images on a small screen. |
Real-World Application
Smartphones are viewed from short distances. At typical usage, 1080p already appears extremely sharp. Higher resolutions may reduce battery life without visible improvement.
Monitors are viewed from medium distances. A 24-inch screen looks excellent at 1080p. Larger monitors benefit from 1440p or 4K for sharper text and more workspace.
Televisions are viewed from farther away. A 32-inch TV works well at 1080p. A 55-inch or larger TV benefits from 4K. 8K becomes noticeable only on very large displays.
Practical clarity is always a balance of resolution, screen size, and distance.
Common Mistakes
Many users assume higher resolution always means better experience. This is not always true.
Buying an 8K TV without 8K content offers no immediate benefit. Using 4K on very small screens may waste power without visible improvement. Running displays at non-native resolutions reduces sharpness. Confusing marketing labels like “2K” leads to wrong purchases.
Understanding resolution in context prevents these mistakes.
Adjustment & Feedback
The best way to understand these concepts is to see them in action on your own hardware. I recommend you start by using our free Screen Resolution Checker. It will instantly show you your current display’s native resolution, its aspect ratio, and other useful details like device pixel ratio.
Once you know your baseline, you can make informed adjustments:
- On your computer, ensure your display is set to its native resolution in system settings for optimal sharpness.
- Experiment with scaling settings if text is too small on a high-resolution display.
- When creating content, use our Aspect Ratio Calculator to preview how your work will appear on different screens.
Also Read: WQHD vs QHD – What’s the Difference, Explained in Simple Terms
Practical Next Steps
- Audit Your Needs: Are you a competitive gamer, a movie enthusiast, or a multitasking professional? Your primary activity points to your ideal resolution tier.
- Check Your Hardware: For PC users, verify your graphics card’s capability for your target resolution and refresh rate. Consult benchmark reviews.
- Test Before You Buy: If possible, view displays in person. Look at text clarity, color vibrancy, and motion handling, not just the spec sheet.
- Use Our Tools: Bookmark our checker tool to diagnose display issues or verify the specs of a new device.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
Display resolution is about choosing the right level of detail for your screen size and usage. Bigger numbers alone do not guarantee better experience. Understanding how 720p, 1080p, 1440p, 4K, 5K, and 8K differ allows smarter decisions, clearer visuals, and efficient hardware use.
Use the tools on WhatIsMyScreenResolution to check, compare, and calculate your ideal setup.